Types Of COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a lung condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes airflow blockages and breathing difficulties. COPD is a term used to describe two primary lung conditions, chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Understanding COPD is crucial to managing the condition effectively. While there is no cure for COPD, early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Risk factors for COPD include smoking, air pollution, and exposure to harmful chemicals. It is essential to identify these risk factors and take steps to reduce exposure to them.
Key Takeaways
- COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes breathing difficulties and airflow blockages.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage COPD symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Risk factors for COPD include smoking, air pollution, and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Understanding COPD
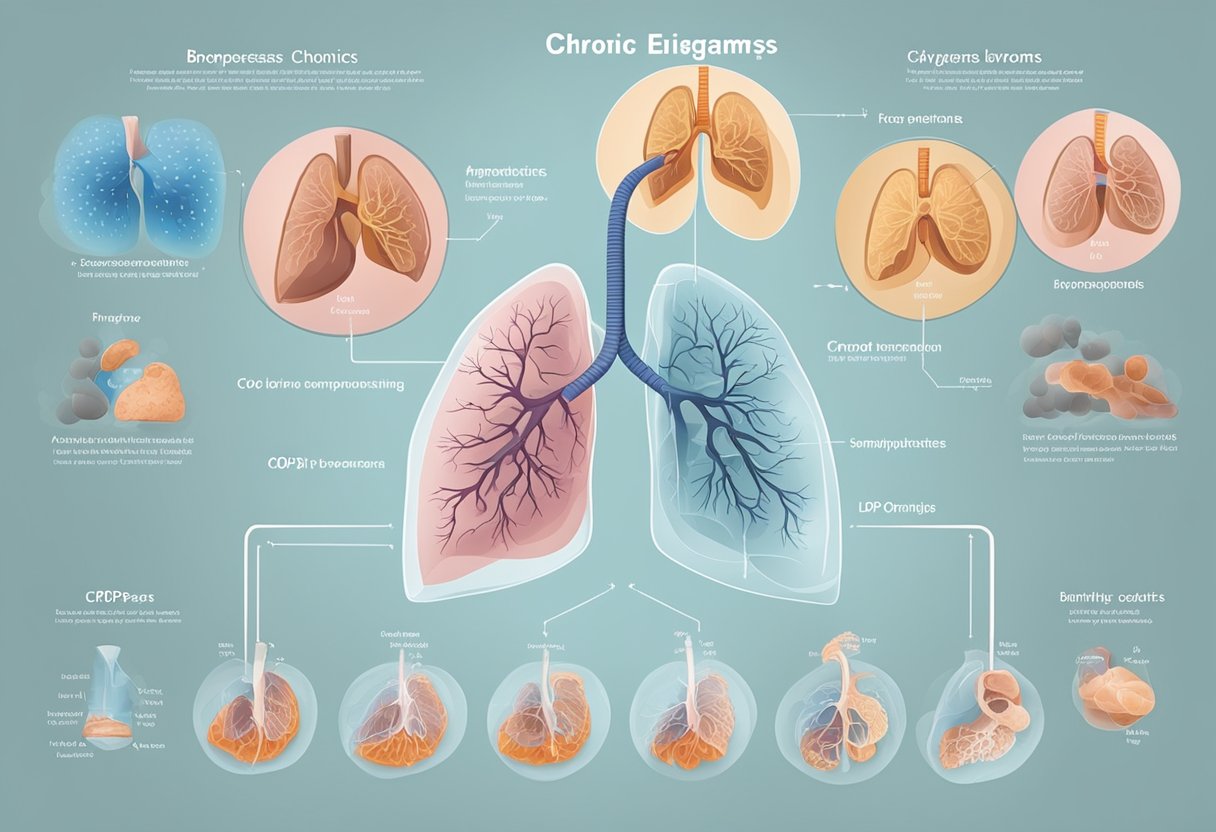
COPD is a chronic lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a progressive disease which means that it gets worse over time. The two most common types of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis is a condition in which the airways in the lungs become inflamed and produce excess mucus. This leads to a persistent cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Emphysema, on the other hand, is a condition in which the air sacs, also known as alveoli, in the lungs are damaged. This leads to difficulty in breathing and decreased lung function.
Pathophysiology of COPD
The pathophysiology of COPD involves a complex interplay between chronic inflammation, structural changes in the lungs, and exposure to noxious particles or gases. Prolonged exposure to cigarette smoke is the most common cause of COPD. Other factors that can contribute to the development of COPD include exposure to air pollution, second-hand smoke, and occupational dust and chemicals.
The inflammation in the airways and lungs in COPD leads to structural changes such as narrowing of the airways and destruction of the alveoli. This results in decreased lung function and difficulty in breathing. The inflammation also leads to the production of excess mucus which further obstructs the airways.
In conclusion, COPD is a chronic lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The two most common types of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The pathophysiology of COPD involves chronic inflammation, structural changes in the lungs, and exposure to noxious particles or gases.
Risk Factors and Causes
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact cause of COPD is not fully understood, there are several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Smoking and Environmental Factors
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, up to 75% of COPD cases are caused by smoking. Other environmental factors that can increase the risk of developing COPD include long-term exposure to air pollution, secondhand smoke, and chemical fumes.
Genetics and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
In some cases, COPD can be caused by genetic factors. People with a family history of COPD are more likely to develop the disease. Additionally, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a genetic condition that can cause COPD. AATD is a rare condition that affects the liver and lungs, and can lead to the development of COPD in people who smoke or are exposed to other environmental factors.
While smoking is the primary cause of COPD, it is important to note that not all smokers develop the disease. Other factors, such as age and overall health, can also play a role in the development of COPD. By understanding the risk factors and causes of COPD, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing this debilitating disease.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
COPD is a chronic lung disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is important to recognize the symptoms of COPD early on so that proper treatment can be administered. COPD symptoms may include cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and the production of mucus.
Recognizing COPD Symptoms
COPD symptoms may be mild at first and progress over time. Some people may not even realize they have COPD until the disease has progressed to a more advanced stage. Therefore, it is important to recognize the early warning signs of COPD. Some common early symptoms of COPD include:
- Chronic cough
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Increased production of mucus
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and improve your quality of life.
Diagnostic Procedures
If you have symptoms of COPD, your doctor may perform some diagnostic tests to determine if you have the disease. These tests may include:
- Spirometry: This test measures how much air you can inhale and exhale and how quickly you can do it. It is the most common test used to diagnose COPD.
- Chest X-ray: This test can show if there are any abnormalities in your lungs, such as emphysema or chronic bronchitis.
- CT scan: This test can provide more detailed images of your lungs and can help your doctor determine the extent of the damage.
Once you have been diagnosed with COPD, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs. Treatment may include medications, such as bronchodilators and steroids, as well as lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and participating in pulmonary rehabilitation.
In conclusion, recognizing the early warning signs of COPD and getting a proper diagnosis is essential for managing the disease and improving your quality of life. If you experience any symptoms of COPD, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment and Management
COPD is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options for COPD include medications, therapies, and surgical interventions.
Medications and Therapies
Bronchodilators are medications that help to open up the airways and improve breathing. They can be delivered through an inhaler or a nebulizer. Inhaled steroids can also be used to reduce inflammation in the airways and improve lung function.
Oxygen therapy may be necessary for people with severe COPD. This involves using a machine to deliver oxygen directly to the lungs. Oxygen therapy can improve symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that includes exercise, education, and support. It can help people with COPD to improve their lung function, reduce symptoms, and increase their overall quality of life.
Surgical Options and Rehabilitation
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat COPD. Lung volume reduction surgery involves removing damaged tissue from the lungs to improve breathing. Lung transplant may also be an option for some people with severe COPD.
Pulmonary rehabilitation can also be an effective treatment option for people with COPD. This program includes exercise, education, and support to help people manage their symptoms and improve their lung function.
Overall, the treatment and management of COPD requires a comprehensive approach that includes medications, therapies, and surgical interventions. By working closely with a healthcare provider, people with COPD can develop an individualized treatment plan that meets their unique needs and improves their overall quality of life.
Living with COPD
Living with COPD can be challenging, but there are ways to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The following subsections provide information on lifestyle changes and support, as well as prevention and potential complications.
Lifestyle Changes and Support
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage COPD symptoms and improve overall health. Regular exercise, for example, can help strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve breathing. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
Avoiding smoke, pollution, fumes, and dust is also important for managing COPD symptoms. Quitting smoking is essential for anyone with COPD, as smoking can worsen symptoms and increase the risk of complications.
Eating a healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight can also help manage COPD symptoms. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains can provide the nutrients and energy needed to maintain a healthy weight and improve overall health.
Joining a support group can also be beneficial for those living with COPD. Support groups can provide emotional support, as well as practical advice on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Prevention and Complications
Preventing complications is an important part of managing COPD. Vaccines can help prevent respiratory infections, which can worsen COPD symptoms and increase the risk of complications. It is important to discuss vaccination options with a healthcare professional.
Complications of COPD can include heart failure, which can be life-threatening. It is important to seek medical attention if experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or swelling in the legs.
In summary, making certain lifestyle changes, joining a support group, and taking preventative measures can help manage COPD symptoms and improve quality of life. Seeking medical attention for complications is also important for maintaining overall health.






