Types Of Feet
Types of feet refer to the various shapes and sizes of human feet, which can differ significantly from person to person. The anatomy of the foot is complex, and its structure can affect not only foot health but also overall health and well-being. A person’s foot type can determine the type of shoes they should wear, the type of exercises they should do, and even the type of sports they should participate in.
There are several types of feet, each with its unique characteristics, including the shape of the toes, the width of the foot, and the height of the arch. The most common foot types are flat feet, high arches, and neutral feet. Flat feet have little or no arch, while high arches have a very defined arch. Neutral feet have a moderate arch, which is considered the ideal foot type.
Understanding the different types of feet is essential for maintaining good foot health and preventing foot problems. It is also important for selecting the right type of shoes and support to help prevent injuries and improve overall foot function. By understanding the anatomy and types of feet, individuals can take steps to improve their foot health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways
- The anatomy of the foot is complex, and its structure can affect not only foot health but also overall health and well-being.
- The most common foot types are flat feet, high arches, and neutral feet.
- Understanding the different types of feet is essential for maintaining good foot health and preventing foot problems.
Anatomy and Types of Feet
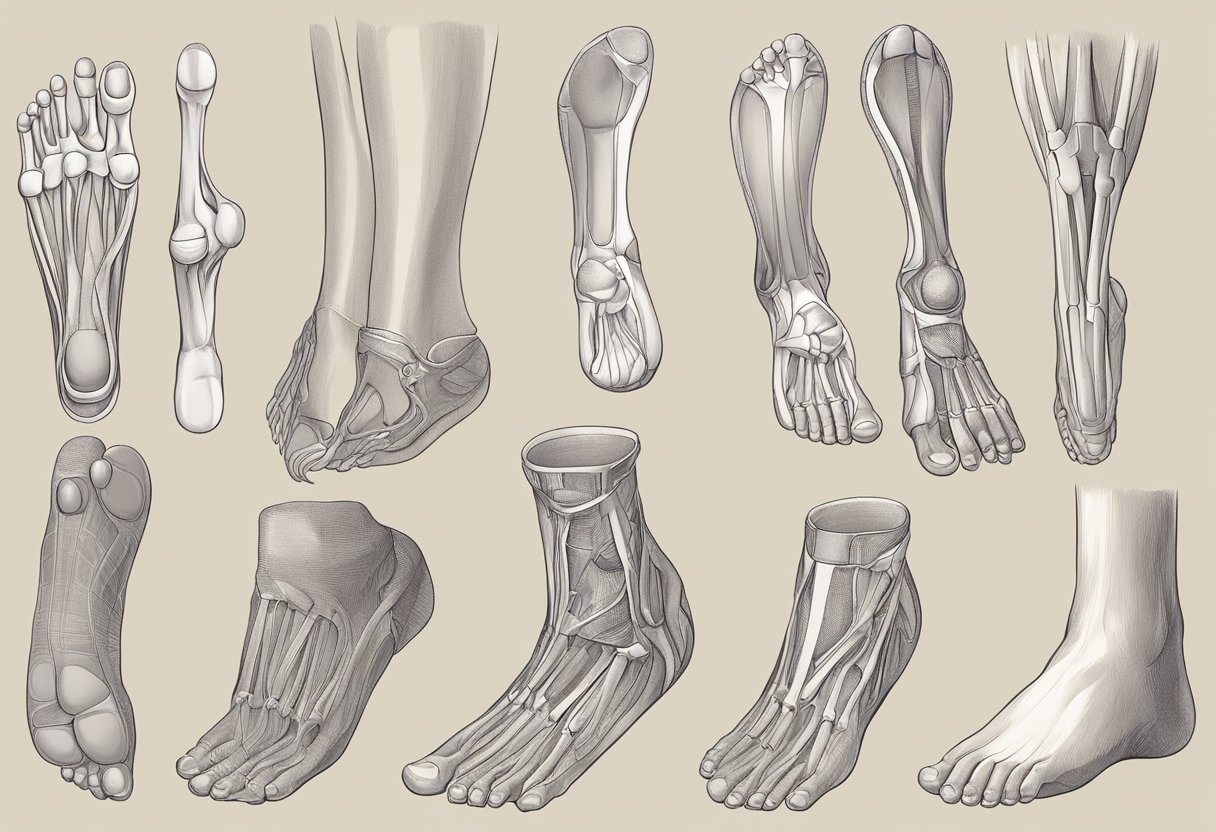
The human foot is a complex structure, consisting of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The foot can be divided into three parts: the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot. The forefoot includes the toes and the ball of the foot, while the midfoot includes the arch and the instep. The hindfoot includes the heel and the ankle.
There are different types of feet, which are characterized by their shape, length, and width. Some of the most common types of feet are the Greek foot, Roman foot, Egyptian foot, Celtic foot, and Peasant foot.
Greek Foot
The Greek foot, also known as the Morton’s toe, is characterized by a longer second toe than the big toe. This type of foot is named after the ancient Greeks, who considered it a sign of beauty and intelligence. The Greek foot is also common among athletes, as it provides extra stability and balance.
Roman Foot
The Roman foot, also known as the Square foot, is characterized by toes that are all the same length. This type of foot is named after the ancient Romans, who considered it a sign of strength and stability. The Roman foot is also common among people who have to stand for long periods of time, as it provides extra support and comfort.
Egyptian Foot
The Egyptian foot, also known as the Peasant foot, is characterized by a longer big toe than the other toes. This type of foot is named after the ancient Egyptians, who considered it a sign of royalty and power. The Egyptian foot is also common among people who have to walk on uneven surfaces, as it provides extra balance and grip.
Celtic Foot
The Celtic foot, also known as the Greek Celtic foot, is characterized by a longer second toe than the big toe and a wider forefoot. This type of foot is named after the ancient Celts, who considered it a sign of beauty and grace. The Celtic foot is also common among people who have to run on uneven surfaces, as it provides extra stability and shock absorption.
Peasant Foot
The Peasant foot, also known as the Egyptian Peasant foot, is characterized by toes that are all the same length and a wider forefoot. This type of foot is named after the peasants who worked in the fields, as it provides extra support and balance. The Peasant foot is also common among people who have to walk long distances, as it provides extra comfort and durability.
In conclusion, the anatomy and types of feet are important to understand for a variety of reasons. By knowing the different types of feet, individuals can better understand their own foot shape and choose the appropriate footwear to support their feet.
Arch Types and Their Impact
The arch of the foot is an important structural component that helps distribute weight and absorb shock during movement. There are four main arch types – high arches, normal arches, low arches, and flat feet. Each arch type has its own unique characteristics and impact on foot health.
High Arches
High arches, also known as cavus foot, are characterized by an elevated arch. Individuals with high arches tend to have a shorter foot length and a wider forefoot. This arch type can put excessive load on the ball and heel of the foot, leading to pain and discomfort. High arches can also cause instability and balance issues, making individuals more susceptible to ankle sprains and other injuries.
Normal Arches
Normal arches, also known as neutral arches, are the most common arch type. The middle part of the arch is about half filled, which means the arch naturally supports the body weight and pronates, or rolls in, under a normal load. Individuals with neutral arches have a lower risk of developing foot problems, but they still need to choose the right footwear to support their arch and prevent injury.
Low Arches
Low arches, also known as flat feet, are characterized by a collapsed arch. The entire sole of the foot makes contact with the ground, and the arch appears to be flat or non-existent. Flat feet can cause overpronation, which means the foot rolls inward excessively during movement. This can put extra strain and stretch on the plantar fascia, making individuals more susceptible to plantar fasciitis. Flat feet can also cause knee, hip, and back pain.
Flat Feet
Flat feet are the most extreme form of low arches. Individuals with flat feet have no visible arch, and their feet appear to be completely flat. Flat feet can cause pain and discomfort in the feet, ankles, knees, hips, and lower back. Individuals with flat feet need to choose footwear that provides adequate arch support and cushioning to prevent injury and reduce pain.
In conclusion, understanding the different arch types and their impact on foot health is crucial for maintaining foot health and selecting the right footwear. Individuals should choose footwear that supports their arch type and provides adequate cushioning to prevent injury and reduce pain.
Foot Conditions and Deformities
Feet are an essential part of the body, and any deformity or condition can cause discomfort and affect mobility. Some of the common foot conditions and deformities are discussed below.
Bunions
Bunions, also known as hallux valgus, are bony bumps that form at the base of the big toe. They occur when the big toe pushes against the next toe, causing the joint to stick out. Bunions can cause pain, swelling, and redness, and can make it difficult to find comfortable shoes.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of bunions, including genetics, wearing ill-fitting shoes, and arthritis. Treatment options for bunions include wearing comfortable shoes, using orthotics or padding, and in severe cases, surgery.
Hammer Toes
Hammer toes, also known as hammertoes, are a deformity of the toes that causes them to bend downwards instead of pointing straight ahead. This can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty walking.
Hammer toes can be caused by genetics, wearing tight shoes, or an injury. Treatment options for hammer toes include wearing comfortable shoes, using orthotics or padding, and in severe cases, surgery.
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a condition that causes pain in the heel and bottom of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed.
Plantar fasciitis can be caused by overuse, wearing shoes with poor arch support, or having tight calf muscles. Treatment options for plantar fasciitis include rest, stretching, using orthotics or padding, and in severe cases, surgery.
In conclusion, foot conditions and deformities can cause discomfort and affect mobility. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any foot pain or discomfort. Treatment options are available, and with proper care, most foot conditions and deformities can be managed effectively.
Footwear and Support
Shoes for Different Foot Types
When it comes to selecting shoes, it is important to consider the type of foot you have. The three main types of feet are flat feet, high-arched feet, and neutral feet. Flat feet have little to no arch, while high-arched feet have a pronounced arch. Neutral feet fall somewhere in between and have a moderate arch. The type of arch you have can impact your gait, foot health, and the type of shoes and support you may need.
For those with flat feet, it is recommended to select shoes with a supportive footbed and a firm midsole to provide stability and prevent overpronation. Shoes with a wide toe box can also be beneficial for increased comfort. High-arched feet, on the other hand, require shoes with extra cushioning and shock absorption to reduce impact and provide support. Neutral feet can benefit from shoes with a combination of cushioning and support.
Orthotics and Insoles
In addition to selecting the right shoes, orthotics and insoles can provide additional support and comfort for those with specific foot needs. Functional orthotics are designed to support abnormal foot biomechanics and can be beneficial for those with flat feet or overpronation. Accommodative orthotics are designed to provide cushioning and support for those with high-arched feet or underpronation.
When selecting orthotics or insoles, it is important to consider the size, shape, and arch support to ensure a proper fit and maximum benefit. Orthotics and insoles can also be beneficial for those with foot conditions such as plantar fasciitis or heel spurs.
Overall, selecting the right footwear and support can greatly impact foot health and comfort. By considering the type of foot and specific needs, individuals can select shoes, orthotics, and insoles that provide the necessary support and cushioning for optimal foot health.
Biomechanics and Gait Analysis
Pronation and Supination
Pronation and supination are two fundamental movements of the foot that are essential for proper gait and posture. Pronation refers to the inward rolling of the foot during weight-bearing activities, while supination is the outward rolling of the foot. Both movements are normal and necessary for proper shock absorption and balance during walking and running.
However, overpronation (excessive inward rolling) or oversupination (excessive outward rolling) can lead to biomechanical imbalances, which may cause pain and discomfort in the feet, ankles, knees, hips, and lower back.
Gait and Posture
Gait analysis is a biomechanical assessment of the way a person walks or runs. It involves the measurement of various parameters such as step length, stride length, foot angle, and joint angles. Gait analysis can help identify abnormal movement patterns that may contribute to pain and injury.
Posture refers to the alignment of the body in relation to gravity. Good posture involves maintaining a neutral spine and proper alignment of the pelvis, hips, knees, and ankles. Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances, joint pain, and back pain.
Gait and posture are closely related, and abnormal gait patterns can lead to poor posture and vice versa. Therefore, a comprehensive biomechanical assessment that includes gait analysis and posture evaluation can help identify the root cause of pain and discomfort and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In conclusion, understanding the biomechanics of the foot and ankle is essential for maintaining proper gait and posture. Pronation and supination are normal movements of the foot that are necessary for shock absorption and balance. However, overpronation or oversupination can lead to biomechanical imbalances and pain. Gait analysis and posture evaluation can help identify abnormal movement patterns and develop an appropriate treatment plan to improve stability, alignment, and balance.






