Types Of Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is a crucial component of the human body, responsible for movement, posture, and various physiological functions. It is composed of cells called myocytes that are specialized to contract and produce force. There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Each type of muscle tissue has unique characteristics and functions that make it well-suited for specific tasks.
Skeletal muscle tissue is the most abundant type of muscle tissue in the body and is responsible for voluntary movement. It is attached to bones by tendons and is striated, meaning it has a striped appearance. Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is also striated, but unlike skeletal muscle tissue, it is involuntary. Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of hollow organs and is responsible for involuntary movement. It is non-striated and has a spindle-like appearance.
Key Takeaways
- Muscle tissue is essential for movement and physiological functions in the body.
- There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each with unique characteristics and functions.
- Skeletal muscle tissue is responsible for voluntary movement, cardiac muscle tissue pumps blood, and smooth muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movement.
Basic Anatomy and Functions of Muscle Tissue
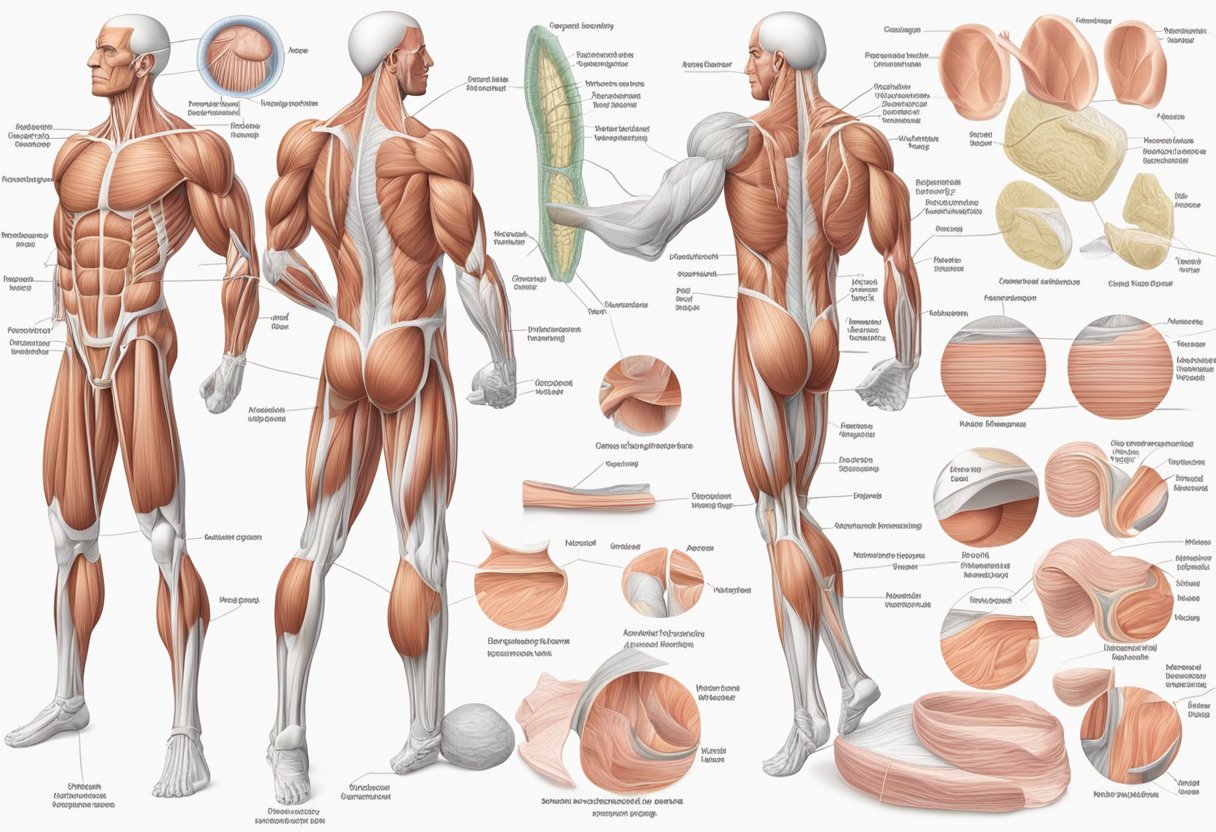
Muscle tissue is a specialized tissue that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. Cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart, and smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
Structure of Muscle Cells
Muscles are made up of muscle fibers, which are long, cylindrical cells that contain many nuclei. Each muscle fiber is composed of myofibrils, which are long, thin structures that contain actin and myosin filaments. Actin and myosin are the proteins responsible for muscle contraction. The myofibrils are arranged in repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the functional units of muscle tissue. The sarcomere is bounded by two Z lines and contains actin and myosin filaments that slide past each other during muscle contraction.
Muscle Contraction Mechanism
Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal from the nervous system. The signal causes the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which binds to the protein troponin and causes a conformational change in tropomyosin. This exposes the active sites on the actin filaments, which allows myosin to bind to actin and form cross-bridges. The energy for muscle contraction comes from the hydrolysis of ATP, which causes the myosin heads to change conformation and pull the actin filaments towards the center of the sarcomere. This shortens the sarcomere and causes muscle contraction.
In conclusion, muscle tissue is a specialized tissue that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. Muscle fibers are long, cylindrical cells that contain many nuclei and are composed of myofibrils, which are long, thin structures that contain actin and myosin filaments. Muscle contraction is initiated by a signal from the nervous system, and the energy for muscle contraction comes from the hydrolysis of ATP.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue is a type of striated muscle tissue that is attached to bones by tendons and is responsible for most voluntary movements in the body. This type of muscle tissue is characterized by its multinucleated cells, which are long and cylindrical in shape. Skeletal muscle tissue is also known as voluntary muscle tissue because it is under conscious control.
Characteristics of Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are composed of muscle fibers that are bundled together into fascicles. Each muscle fiber is a single cell with multiple nuclei that are located just beneath the cell membrane. The nuclei help to control the activity of the muscle fiber by regulating the production of proteins and other cellular components.
Skeletal muscles are also richly supplied with blood vessels and nerves, which enter the muscle tissue at the neuromuscular junction. This junction is where the nerve fibers release neurotransmitters that stimulate the muscle fibers to contract.
Role in Movement and Posture
Skeletal muscles play a major role in movement and posture. When a skeletal muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone to which it is attached, causing movement at the joint. For example, the biceps muscle in the upper arm contracts to lift the forearm towards the shoulder.
Skeletal muscles also help to maintain posture by stabilizing the bones and joints of the body. Without the support of skeletal muscles, the body would collapse under its own weight.
In summary, skeletal muscle tissue is a specialized type of muscle tissue that is responsible for most voluntary movements in the body. It is characterized by its multinucleated cells and striated appearance. Skeletal muscles play a major role in movement and posture, making them essential for everyday activities.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the three types of muscle tissue in the human body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle tissue. The unique feature of cardiac muscle tissue is its ability to contract rhythmically and involuntarily without fatigue. This property is essential for the continuous pumping of blood throughout the body.
Unique Features of Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle cells, also known as cardiomyocytes, are cylindrical in shape and contain a single nucleus. Unlike skeletal muscle cells, which have multiple nuclei, cardiac muscle cells are connected to each other through intercalated discs. These discs allow for the synchronized contraction of the entire heart muscle.
Another unique feature of cardiac muscle tissue is the presence of pacemaker cells. These cells are responsible for initiating and regulating the heartbeat. They generate electrical impulses that spread throughout the heart and trigger the contraction of the cardiac muscle cells.
Cardiac Muscle in Circulatory Function
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body. The cardiac muscle tissue is responsible for the rhythmic and involuntary contraction of the heart, which allows it to pump blood effectively. The heart has four chambers: the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it into the right ventricle. The right ventricle then pumps the blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the left atrium and is pumped into the left ventricle. The left ventricle then pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
In conclusion, cardiac muscle tissue is a specialized type of muscle tissue that is responsible for the rhythmic and involuntary contraction of the heart. The unique features of cardiac muscle tissue, such as intercalated discs and pacemaker cells, allow for the synchronized contraction of the entire heart muscle. The cardiac muscle tissue plays a vital role in the circulatory system by ensuring the effective pumping of blood throughout the body.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Smooth muscle tissue is a type of non-striated muscle tissue that is found in the walls of various organs and structures throughout the body. It is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs, such as the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems, as well as the airways and blood vessels.
Smooth Muscle in Organ Systems
Smooth muscle tissue is found in various organs and structures throughout the body. In the digestive system, smooth muscle is responsible for the movement of food through the digestive tract. The muscular walls of the stomach and intestines are composed of smooth muscle tissue. In the reproductive system, smooth muscle tissue is found in the uterus and fallopian tubes, where it helps to move the egg and sperm towards each other.
Smooth muscle tissue is also found in the walls of blood vessels, where it helps to regulate blood flow and blood pressure. The contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle cells in the walls of blood vessels can cause the vessels to constrict or dilate, which affects blood flow and blood pressure.
Regulation and Control of Smooth Muscle
The contraction of smooth muscle tissue is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary actions in the body. The autonomic nervous system consists of two branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response in the body, which prepares the body for action in response to a perceived threat. When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, it causes the smooth muscle tissue to contract, which can cause various physiological changes in the body.
The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, is responsible for the “rest and digest” response in the body, which promotes relaxation and digestion. When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it causes the smooth muscle tissue to relax, which can promote digestion and other restful activities in the body.
In conclusion, smooth muscle tissue is an important type of muscle tissue that is responsible for involuntary movements in various organs and structures throughout the body. Its contraction is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary actions in the body.
Physiological Properties of Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is a specialized tissue that enables movement in the human body. It is characterized by four main properties: excitability, contractibility, elasticity, and extensibility. These properties are essential for muscle tissue to function properly and carry out its physiological functions.
Excitability and Contractibility
Excitability is the ability of muscle tissue to respond to stimuli. This property is crucial for muscle tissue to receive signals from the nervous system and initiate muscle contractions. The nervous system sends electrical signals, called action potentials, to muscle tissue, which triggers the release of calcium ions that enable muscle contraction.
Contractibility, on the other hand, is the ability of muscle tissue to shorten and generate force. This property is what allows muscle tissue to perform its primary function of movement. When muscle tissue receives a signal from the nervous system, it contracts and generates force, which results in movement.
Elasticity and Extensibility
Elasticity is the ability of muscle tissue to return to its original shape after being stretched. This property is essential for muscle tissue to maintain its structure and function properly. When muscle tissue is stretched, it stores elastic energy, which is released when the muscle tissue returns to its original shape.
Extensibility, on the other hand, is the ability of muscle tissue to stretch and extend beyond its resting length. This property is crucial for muscle tissue to adapt to changes in the body and perform its physiological functions. When muscle tissue is stretched beyond its resting length, it generates tension, which is essential for movement.
In conclusion, muscle tissue is a specialized tissue that enables movement in the human body. Its physiological properties, including excitability, contractibility, elasticity, and extensibility, are essential for muscle tissue to function properly and carry out its physiological functions. These properties are closely related to the nervous system, action potential, and contractile mechanisms of muscle tissue.






