Types Of Skin Cancer on the Face
Skin cancer is an abnormal growth of skin cells, which can develop anywhere on the body, including the face. The face is particularly susceptible to skin cancer because it is the most exposed part of the body to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. There are different types of skin cancer that can affect the face, and early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.
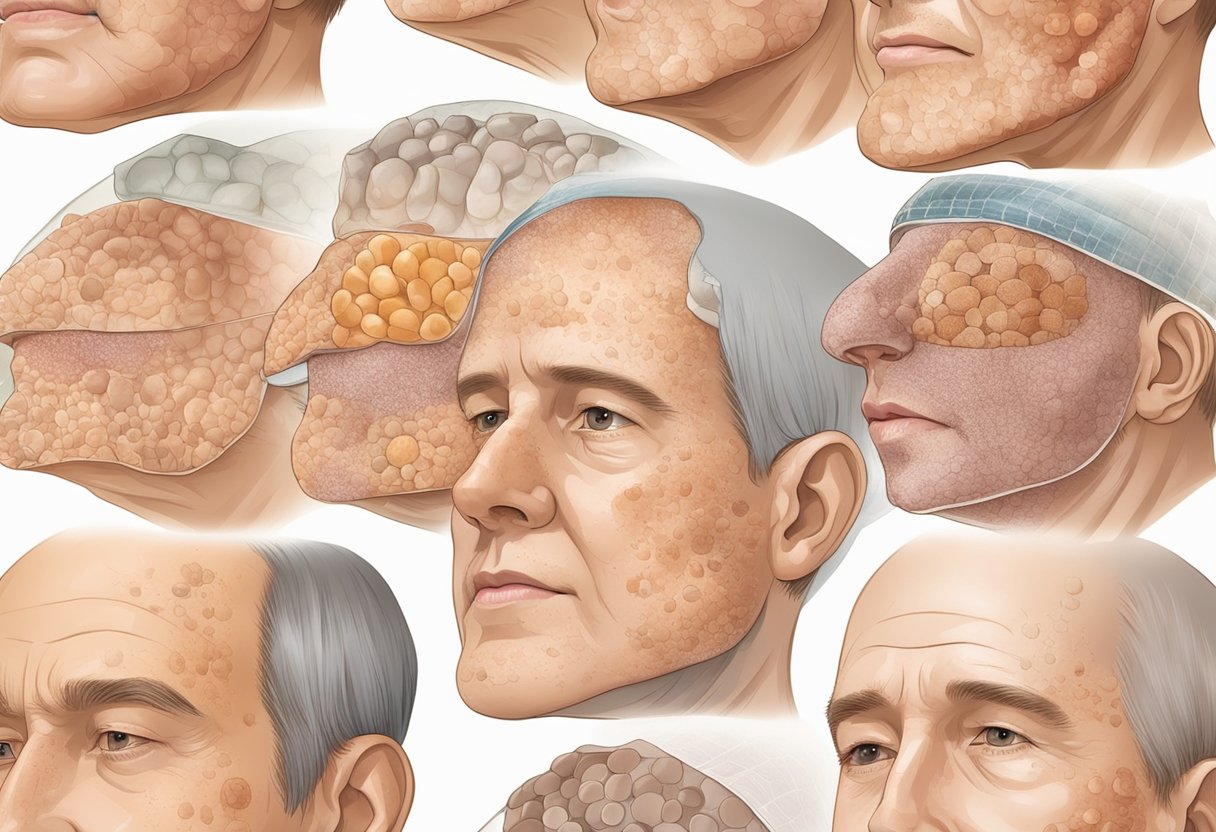
The three most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma. BCC is the most common type of skin cancer on the face, and it often appears as a flesh-colored, pearly bump or a pinkish patch of skin. SCC is less common but can also develop on the face, appearing as a scaly red patch or a wart-like growth. Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer, and although it is less common than BCC and SCC, it can still develop on the face.
Key Takeaways:
- Skin cancer can develop anywhere on the body, including the face, which is particularly susceptible to it due to sun exposure.
- The three most common types of skin cancer on the face are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
- Early detection and treatment of skin cancer on the face are crucial for successful outcomes.
Understanding Skin Cancer
Types of Skin Cancer on the Face
Skin cancer is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The face is one of the most common areas where skin cancer develops due to the high exposure to the sun. There are several types of skin cancer that can affect the face, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, sebaceous gland carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer that affects the face. It usually appears as a red, rough, or dry, scaly patch of skin that may itch or bleed. Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer that affects the face. It usually appears as a raised, rough, or scaly patch of skin that may be painful and bleed.
Melanoma is a less common but more aggressive type of skin cancer that can develop on the face. It often appears as a dark, irregularly shaped mole that may change in size, shape, or color over time. Other types of skin cancer that can affect the face include Merkel cell carcinoma, sebaceous gland carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of skin cancer on the face may vary depending on the type of cancer and its stage. However, some common signs and symptoms include red, rough, or dry, scaly patches of skin that may itch or bleed, tan, black, white, pink, or brown spots or moles that may be flat or raised, painless, hard bumps that may have an irregular border or asymmetry, and so on.
It is important to note that not all skin changes are cancerous. However, if you notice any unusual changes in your skin, such as new growths, sores that do not heal, or changes in the color, shape, or size of existing moles or spots, you should consult a dermatologist or a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Risk Factors and Causes
Skin cancer on the face can be caused by a variety of factors, both genetic and environmental. Understanding these risk factors is important in preventing the development of skin cancer.
Sun Exposure and Protection
One of the primary causes of skin cancer on the face is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UVA and UVB rays can cause damage to skin cells, leading to the development of cancer. It is important to protect your skin from the sun by wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and hats, and using sunscreen with a high SPF rating. Sunglasses can also help protect your eyes from UV radiation.
Indoor tanning is another risk factor for skin cancer, as it exposes the skin to high levels of UV radiation. It is recommended to avoid indoor tanning altogether.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Fair-skinned individuals are at a higher risk for developing skin cancer on the face, as their skin is more susceptible to damage from UV radiation. Older individuals and those who have undergone organ transplants or have HIV are also at a higher risk.
Other environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals or radiation, can also increase the risk of developing skin cancer on the face.
In conclusion, protecting your skin from the sun and avoiding indoor tanning are crucial in preventing skin cancer on the face. Understanding your individual risk factors, such as fair skin or a history of organ transplants, can also help you take steps to prevent skin cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Professional Diagnosis
Diagnosis of skin cancer on the face requires the expertise of a dermatologist or a doctor who specializes in skin diseases. The professional will conduct a thorough examination of the affected area and may also recommend a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. During the biopsy, a small sample of the skin tissue will be removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis. If the biopsy confirms the presence of skin cancer, the doctor will discuss the available treatment options with the patient.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for skin cancer on the face, and the choice of treatment will depend on the type and stage of cancer. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that patients with skin cancer on the face should seek treatment from a board-certified dermatologist who has experience in treating skin cancer.
The treatment options for skin cancer on the face include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery is the most common treatment option and involves removing the cancerous tissue from the face. In some cases, the surgeon may also remove a small amount of healthy tissue surrounding the cancerous tissue to ensure that all of the cancer is removed.
Radiation therapy involves using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. This treatment option is often used in conjunction with surgery to ensure that all of the cancer is removed.
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. This treatment option is often used for advanced cases of skin cancer on the face.
In conclusion, skin cancer on the face requires prompt diagnosis and treatment by a professional. The available treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, and the choice of treatment will depend on the type and stage of cancer. Patients should seek treatment from a board-certified dermatologist with experience in treating skin cancer.
Prevention and Early Detection
Skin cancer on the face can be prevented by taking protective measures against the sun’s harmful UV radiation. Regular skin checks and self-examination can help in early detection of skin cancer.
Protective Measures
Protective measures can be taken to prevent skin cancer on the face. These include:
- Wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and hats with wide brims that shade the face, ears, and neck from the sun’s rays.
- Wearing sunglasses that block 99% to 100% of UVA and UVB radiation.
- Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on the face, neck, and ears. Sunscreen should be applied 15 minutes before sun exposure and reapplied every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
- Avoiding sun exposure during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when the sun’s rays are strongest.
Regular Skin Checks
Regular skin checks and self-examination can help in early detection of skin cancer. People should examine their skin once a month and get familiar with any freckles, moles, and other marks. Any changes in size, shape, color, or texture of a mole or other skin lesion should be reported to a doctor immediately.
People who are at higher risk of skin cancer, such as those with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer, should have regular skin checks by a dermatologist.
In conclusion, taking protective measures against the sun’s harmful UV radiation, wearing protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen, and regular skin checks and self-examination can help in the prevention and early detection of skin cancer on the face.
Living with Skin Cancer
Living with skin cancer can be challenging, but it is possible to manage the symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. There are several strategies that can help individuals with skin cancer on their face cope with their condition.
Managing Symptoms
One of the most important aspects of managing skin cancer symptoms is to follow the treatment plan recommended by the doctor. This may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
In addition to medical treatments, there are several self-care strategies that can help manage symptoms. For example, using a moisturizer can help prevent dryness and itching caused by radiation therapy. Pain management techniques such as relaxation exercises, acupuncture, or massage therapy can also be helpful.
Support and Resources
Living with skin cancer can be emotionally challenging, and it is important to have a support system in place. Support groups can provide a safe and confidential environment for individuals to share their experiences and feelings with others who are going through similar situations.
There are also several online resources available for people with skin cancer, including the American Cancer Society’s Coronavirus Resource Center. This resource provides up-to-date information on how to manage cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In conclusion, living with skin cancer on the face can be challenging, but it is possible to manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. By following medical treatments, self-care strategies, and seeking support from others, individuals with skin cancer can successfully manage their condition.






